Concurrent
Concurrent Features
import App from 'App'
import * as ReactDOM from 'react-dom'
// Create a root by using ReactDOM.createRoot():
const root = ReactDOM.createRoot(document.getElementById('app'))
// Render the main <App/> element to the root:
root.render(<App />)
Batching Updates
- All updates will be automatically batched, including updates inside of promises, async code and native event handlers.
ReactDOM.flushSynccan opt-out of automatic batching.
function handleClick() {
// React 17: Re-rendering happens after both of the states are updated.
// This is called batching.
// This is also the default behavior of React 18.
setIsBirthday(b => !b)
setAge(a => a + 1)
}
// For the following code blocks,
// React 18 does automatic batching, but React 17 doesn't.
// 1. Promises:
function handleClick() {
fetchSomething().then(() => {
setIsBirthday(b => !b)
setAge(a => a + 1)
})
}
// 2. Async code:
setInterval(() => {
setIsBirthday(b => !b)
setAge(a => a + 1)
}, 5000)
// 3. Native event handlers:
element.addEventListener('click', () => {
setIsBirthday(b => !b)
setAge(a => a + 1)
})
Reconciler 注册调度任务时, 会通过节流与防抖提升调度性能:
- 在 Task 注册完成后, 会设置
FiberRoot的属性, 代表现在已经处于调度进行中. - 再次进入
ensureRootIsScheduled时 (比如连续 2 次setState, 第二次setState同样会触发 Reconciler 与 Scheduler 执行), 如果发现处于调度中, 则会通过节流与防抖, 保证调度性能. - 节流:
existingCallbackPriority === newCallbackPriority, 新旧更新的优先级相同, 则无需注册新 Task, 继续沿用上一个优先级相同的 Task, 直接退出调用. - 防抖:
existingCallbackPriority !== newCallbackPriority, 新旧更新的优先级不同, 则取消旧 Task, 重新注册新 Task.
function ensureRootIsScheduled(root: FiberRoot, currentTime: number) {
const existingCallbackNode = root.callbackNode
const nextLanes = getNextLanes(
root,
root === workInProgressRoot ? workInProgressRootRenderLanes : NoLanes,
)
if (nextLanes === NoLanes) {
if (existingCallbackNode !== null)
cancelCallback(existingCallbackNode)
root.callbackNode = null
root.callbackPriority = NoLane
return
}
const newCallbackPriority = getHighestPriorityLane(nextLanes)
const existingCallbackPriority = root.callbackPriority
// Debounce.
if (existingCallbackPriority === newCallbackPriority) {
// The priority hasn't changed. We can reuse the existing task. Exit.
return
}
// Throttle.
if (existingCallbackNode != null) {
// Cancel the existing callback. We'll schedule a new one below.
cancelCallback(existingCallbackNode)
}
// Schedule a new callback.
let newCallbackNode
if (newCallbackPriority === SyncLane) {
if (root.tag === LegacyRoot)
scheduleLegacySyncCallback(performSyncWorkOnRoot.bind(null, root))
else scheduleSyncCallback(performSyncWorkOnRoot.bind(null, root))
if (supportsMicroTasks) {
scheduleMicroTask(() => {
if (executionContext === NoContext)
flushSyncCallbacks()
})
} else {
scheduleCallback(ImmediateSchedulerPriority, flushSyncCallbacks)
}
newCallbackNode = null
} else {
const eventPriority = lanesToEventPriority(nextLanes)
const schedulerPriorityLevel
= eventPriorityToSchedulePriority(eventPriority)
newCallbackNode = scheduleCallback(
schedulerPriorityLevel,
performConcurrentWorkOnRoot.bind(null, root),
)
}
root.callbackPriority = newCallbackPriority
root.callbackNode = newCallbackNode
}
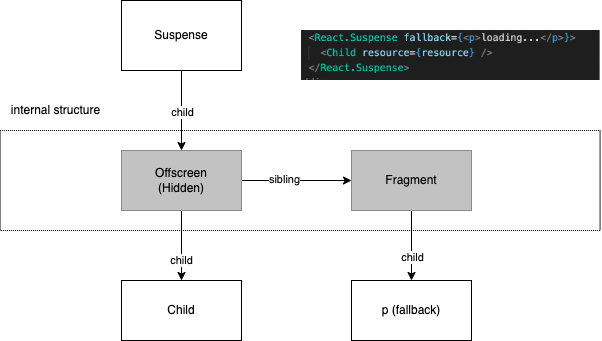
Suspense
Extract loading/skeleton/placeholder components into single place:
export default function App() {
return (
<Suspense fallback={<Skeleton />}>
<Header />
<Suspense fallback={<ListPlaceholder />}>
<ListLayout>
<List pageId={pageId} />
</ListLayout>
</Suspense>
</Suspense>
)
}
React Bottlenecks
- CPU bottleneck: Concurrency Feature (Priority Interrupt Mechanism).
- I/O bottleneck: Suspense.
Error Boundary Suspense
function ErrorFallback() {
return (
<div
className="text-red-500 w-screen h-screen flex flex-col justify-center items-center"
role="alert"
>
<h2 className="text-lg font-bold">Oops, something went wrong :( </h2>
<Button
className="mt-4"
onClick={() => window.location.assign(window.location.origin)}
>
Refresh
</Button>
</div>
)
}
interface AppProviderProps {
children: React.ReactNode
}
export function AppProvider({ children }: AppProviderProps) {
return (
<React.Suspense
fallback={(
<div className="h-screen w-screen flex items-center justify-center">
<Spinner size="xl" />
</div>
)}
>
<ErrorBoundary FallbackComponent={ErrorFallback}>
{children}
</ErrorBoundary>
</React.Suspense>
)
}
Lazy Suspense
Lazy loading and code splitting:
import { lazy, Suspense } from 'react'
const Product = lazy(() => import('./ProductHandler'))
export default function App() {
return (
<div className="product-list">
<h1>My Awesome Product</h1>
<Suspense fallback={<h2>Product list is loading...</h2>}>
<p>Take a look at my product:</p>
<section>
<Product id="PDT-49-232" />
<Product id="PDT-50-233" />
<Product id="PDT-51-234" />
</section>
</Suspense>
</div>
)
}
const { lazy, Suspense } = React
const Lazy = lazy(
() =>
new Promise((resolve) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve({ default: () => <Resource /> })
}, 4000)
}),
)
function Resource() {
return (
<div className="box">
<h1>React Lazy</h1>
<p>
This component loaded after 4 seconds, using React Lazy and Suspense
</p>
</div>
)
}
export default function App() {
return (
<Suspense fallback={<div>Loading...</div>}>
<Lazy />
</Suspense>
)
}
ReactDOM.createRoot(document.getElementById('root')).render(<App />)
function createModuleLoader(load) {
return {
module: null,
promise: null,
error: null,
load() {
if (this.module != null) {
return this.module
}
if (this.error != null) {
throw this.error
}
if (this.promise == null) {
this.promise = load().then((res) => {
// suppose we get an ES module
this.module = res.default
}, (error) => {
this.error = error
})
}
throw this.promise
}
}
}
function lazy(load) {
const moduleLoader = createModuleLoader(load)
return function (props) {
const Component = moduleLoader.load()
return <Component {...props} />
}
}
SSR Suspense
React v18+: enable Suspense on the server:
- Selective Hydration: one slow part doesn't slow down whole page.
- Streaming HTML: show initial HTML early and stream the rest HTML.
- Enable code splitting for SSR.
export default function LandingPage() {
return (
<div>
<FastComponent />
<Suspense fallback={<Spinner />}>
<Comments />
</Suspense>
</div>
)
}
- Suspense is serialized by comment node with
<!--$-->meaning non-suspended, and<!--$!-->as suspended. - Hydration for Suspense is 2-pass process in order to put it into lower priority.
- During hydration:
- If pre-existing DOM is fallback, then it'll be discarded and client-side rendering will generate the new DOM, either fallback or contents.
- If pre-existing DOM is contents, but client-side suspends. We want to switch the contents directly without fallback in the middle, so fallback won't be displayed.
- If pre-existing DOM is contents and also is the client-side, then hydration continues to the children of Suspense.
import * as React from 'react'
import './style.css'
function createCounter(delay) {
return {
data: null,
promise: null,
fetch() {
if (this.data != null) {
return this.data
}
if (this.promise == null) {
this.promise = new Promise((resolve) => {
setTimeout(() => {
this.data = delay
resolve(this.data)
}, delay)
})
}
throw this.promise
},
}
}
const counter1000 = createCounter(1000)
const counter2000 = createCounter(2000)
function Component({ counter }) {
const count = counter.fetch()
return (<button type="button">{count}</button>)
}
function render(jsx, context) {
if (jsx == null) {
return ''
}
if (typeof jsx === 'string' || typeof jsx === 'number') {
return jsx
}
if (typeof jsx.type === 'string') {
return `<${jsx.type}>${render(jsx.props.children, context)}</${jsx.type}>`
}
if (Array.isArray(jsx)) {
return jsx.map(item => render(item, context)).join('')
}
if (typeof jsx.type === 'function') {
return render(jsx.type(jsx.props), context)
}
if (jsx.type === Symbol.for('react.suspense')) {
try {
return `<div hidden id="S:${context.id}">${render(
jsx.props.children,
context
)}</div><script>TODO: some script to kick off the re-render of target suspense boundary</script>`
} catch (e) {
if ('then' in e) {
const currentContext = { ...context }
e.then(() => {
context.pipe(render(jsx, currentContext))
})
return `<!--$?--><template id="B:${context.id++}"></template>${render(
jsx.props.fallback,
context
)}<!--/$-->`
} else {
throw new Error(`error in rendering:${e}`)
}
}
}
throw new Error(`unhandled type${jsx.type}`)
}
function renderToPipe(jsx, pipe) {
pipe(
render(jsx, {
pipe,
id: 0, // increment id to differentiate suspense boundaries.
})
)
}
export default function App() {
const [chunks, setChunks] = React.useState([])
const pipe = React.useCallback((chunk) => {
console.log('pipe', chunk)
setChunks(chunks => [...chunks, chunk])
}, [])
React.useEffect(() => {
const jsx = (
<div>
<React.Suspense fallback="loading">
<Component counter={counter1000} />
</React.Suspense>
<React.Suspense fallback="loading">
<Component counter={counter2000} />
</React.Suspense>
<p>another p</p>
</div>
)
renderToPipe(jsx, pipe)
}, [pipe])
return (
<div>
{chunks.map((chunk, i) => (
<div key={chunk.id}>
<p>
chunk
{i + 1}
</p>
<code>{chunk}</code>
<hr />
</div>
))}
</div>
)
}