JavaScript Performance Notes
Effective JavaScript
Memory Leak
- Useless global vars (bind to window or document).
- Useless DOM reference.
- Incorrect closure.
- Unnecessary closure creation: 闭包会保留它们包含函数的作用域, 所以比其他函数更占用内存.
- Useless callback functions.
- Forgotten timer from
setTimeout/setInterval: clear withclearTimeout/clearInterval.
- Forgotten tick timer.
- Forgotten event listener:
clear with
removeEventListener. - Forgotten subscriber:
clear with
unsubscribe(id). - Forgotten console log:
clear with
babel/tsc. - Forgotten
Set/Map:WeakSet/WeakMapdon't bother GC. - Circular reference.
- Bad
deleteOperator:delete操作符并不会释放内存, 而且会使得附加到对象上的hidden class(V8为了优化属性访问时间而创建的隐藏类) 失效, 让对象变成slow object.
Danger Features
eval().with () {}.new Function().
Function Performance
Local Variables Performance
- 局部变量引用全局变量/全局变量作为参数传入函数: 加快符号解析.
- 局部变量缓存 DOM 元素.
- 局部变量缓存布局信息.
- 局部变量引用嵌套成员: 加快原型链查找.
- 局部变量引用方法时, 应注意会动态改变 this 指针.
const DOM = tazimi.util.Dom
DOM.method.call(/* 关注 this 指针 */)
Scope Chain Performance
由于作用域链的关系, 标识符解析时, 寻找局部变量速度远快于寻找全局变量速度 (作用域链越长, 查找变量所需时间越长). 故应将全局变量作为参数传入函数进行调用, 不但效率高, 而且易于维护与测试. 即利用局部变量引用全局变量, 加快标识符解析.
Memoization Function
function memoize(fn) {
return (
(cache = Object.create(null)) =>
(...args) => {
return cache[args] || (cache[args] = fn(...args))
}
)()
}
const memoizedGetDistance = memoize(getDistance)
memoizedGetDistance('Murcia', 'Madrid') // => computed, slow
memoizedGetDistance('Murcia', 'Madrid') // => cached, fast!
Loop Performance
倒序循环可提升性能:
for (let i = item.length; i--;)
process(items[i])
let j = items.length
while (j--)
process(items[i])
let k = items.length
do
process(items[k])
while (k--)
Duff's Device:
let i = items.length % 8
while (i)
process(items[i--])
i = Math.floor(items.length / 8)
while (i) {
process(items[i--])
process(items[i--])
process(items[i--])
process(items[i--])
process(items[i--])
process(items[i--])
process(items[i--])
process(items[i--])
}
Math Performance
Bit Operators
i%2=>i&0x1.- 位掩码
const OPTION_A = 1
const OPTION_B = 2
const OPTION_C = 4
const OPTION_D = 8
const OPTION_E = 16
const options = OPTION_A | OPTION_C | OPTION_D
Reduce Repeat Manipulation
- 特性/浏览器检测代码只运行一次.
- 惰性定义模式/自定义模式.
Timer Performance
JavaScript 代码与 UI 共享线程.
setTimeout/setInterval:
- 第二个参数: 不是执行时间, 是加入执行队列时间.
- 若其他位于执行队列中的函数执行时间超过延时, 则用户感觉不到延时的存在.
- 模拟有间隙的循环, 使得 UI 更新得以进入浏览器线程的执行队列中.
- 通过 MicroTask/MicroTask 实现时间分片调度器,
使得长任务不阻塞页面操作 (60 FPS):
e.g React Scheduler and Reconciler, Vue
nextTickAPI.
const button = document.getElementById('myButton')
button.onclick = function () {
oneMethod()
setTimeout(() => {
document.getElementById('notice').style.color = 'red'
}, 250)
}
/*
* usage: start -> stop -> getTime
*/
const Timer = {
_data: {},
start(key) {
Timer._data[key] = new Date()
},
stop(key) {
const time = Timer._data[key]
if (time)
Timer._data[key] = new Date() - time
},
getTime(key) {
return Timer._data[key]
},
}
function pollTimerTask(time) {
if (timerQueue.length === 0)
return
while (timerQueue[0] && time >= timerQueue[0].time) {
const timer = timerQueue.shift()
while (timer.tickerQueue.length) {
const { id, callback, delay, loop, defer } = timer.tickerQueue.shift()
callback(time)
if (loop && idPool[id].exist) {
let nextTime = timer.time + delay
// 当回调函数执行时间超过多个执行周期时
if (time - nextTime > delay) {
nextTime = nextTime + Math.floor((time - nextTime) / delay) * delay
// 延迟执行时, 将 nextTime 推迟至下一个执行周期
defer && (nextTime += delay)
}
registerTimerWithId({
id,
callback,
time: nextTime,
delay,
loop,
defer,
})
} else {
// 当回调函数不需要周期执行或在回调函数中执行 unregister 时
delete idPool[id]
}
}
}
}
Time Slicing
function saveDocument(id) {
// 利用闭包封装待执行任务
const tasks = [openDocument, writeText, closeDocument, updateUI]
setTimeout(function sliceTask() {
// 执行下一个任务
const task = tasks.shift()
task(id)
// 检查是否还有其他任务
if (tasks.length > 0) {
// 递归调用(每次参数不同)
setTimeout(sliceTask, 25)
}
}, 25)
}
function processArray(items, process, callback) {
// 克隆原数组
const todo = items.concat()
setTimeout(function sliceTask() {
process(todo.shift())
if (todo.length > 0)
setTimeout(sliceTask, 25)
else
callback(items)
}, 25)
}
Task Batching and Scheduling
Prioritized task scheduler API:
async function saveSettings() {
const tasks = [
validateForm,
showSpinner,
saveToDatabase,
updateUI,
sendAnalytics,
]
let deadline = performance.now() + 50
while (tasks.length > 0) {
if (
navigator.scheduling?.isInputPending()
|| performance.now() >= deadline
) {
// 1. Pending user input.
// 2. deadline has been reached.
// Yield here:
await yieldToMain()
// Extend the deadline.
deadline += 50
continue
}
// Run task.
const task = tasks.shift()
task()
}
}
function yieldToMain() {
return new Promise((resolve) => {
setTimeout(resolve, 0)
})
}
Debounce and Throttle
防抖动和节流本质是不一样的:
debounce: 防抖动是将多次执行变为最后一次执行 (可用于检测某个连续的 DOM 操作结束, 如resize/scroll停止).throttle: 节流是将多次执行变成每隔一段时间执行 (保证一定时间内只执行一次).
Simple debounce:
function debounce(action, delay) {
let timer = null
return function () {
if (timer)
clearTimeout(timer)
timer = setTimeout(() => {
action()
}, delay)
}
}
Simple throttle:
function throttle(action) {
let isRunning = false
return function () {
if (isRunning)
return
isRunning = true
window.requestAnimationFrame(() => {
action()
isRunning = false
})
}
}
function throttle(func, timeFrame) {
let lastTime = 0
return function (...args) {
const now = new Date()
if (now - lastTime >= timeFrame) {
func(...args)
lastTime = now
}
}
}
Lodash debounce:
// 这个是用来获取当前时间戳的
function now() {
return +new Date()
}
/**
* 防抖函数, 返回函数连续调用时, 空闲时间必须大于或等于 wait, func 才会执行
*
* @param {Function} func 回调函数
* @param {number} wait 表示时间窗口的间隔
* @param {boolean} immediate 设置为 true 时, 是否立即调用函数
* @return {Function} 返回客户调用函数
*/
function debounce(func, wait = 50, immediate = true) {
let timer, context, args
// 延迟执行函数
const later = () =>
setTimeout(() => {
// 延迟函数执行完毕, 清空缓存的定时器序号
timer = null
// 延迟执行的情况下, 函数会在延迟函数中执行
// 使用到之前缓存的参数和上下文
if (!immediate) {
func.apply(context, args)
context = args = null
}
}, wait)
// 这里返回的函数是每次实际调用的函数
return function (...params) {
// 如果没有创建延迟执行函数 (later), 就创建一个
if (!timer) {
timer = later()
// 如果是立即执行, 调用函数
// 否则缓存参数和调用上下文
if (immediate) {
func.apply(this, params)
} else {
context = this
args = params
}
} else {
// 如果已有延迟执行函数 (later), 调用的时候清除原来的并重新设定一个
// 这样做延迟函数会重新计时
clearTimeout(timer)
timer = later()
}
}
}
Lodash throttle:
/**
* Lodash 节流函数, 返回函数连续调用时, func 执行频率限定为 次 / wait
*
* @param {Function} func 回调函数
* @param {number} wait 表示时间窗口的间隔
* @param {object} options 如果想忽略开始函数的的调用, 传入{leading: false}.
* 如果想忽略结尾函数的调用, 传入{trailing: false}
* 两者不能共存, 否则函数不能执行
* @return {Function} 返回客户调用函数
*/
_.throttle = function (func, wait, options) {
let context, args, result
let timeout = null
// 之前的时间戳
let previous = 0
// 如果 options 没传则设为空对象
if (!options)
options = {}
// 定时器回调函数
const later = function () {
// 如果设置了 leading, 就将 previous 设为 0
// 用于下面函数的第一个 if 判断
previous = options.leading === false ? 0 : _.now()
// 置空一是为了防止内存泄漏, 二是为了下面的定时器判断
timeout = null
result = func.apply(context, args)
if (!timeout)
context = args = null
}
return function (...original_args) {
// 获得当前时间戳
const now = _.now()
// 首次进入前者肯定为 true
// 如果需要第一次不执行函数
// 就将上次时间戳设为当前的
// 这样在接下来计算 remaining 的值时会大于0
if (!previous && options.leading === false)
previous = now
// 计算剩余时间
const remaining = wait - (now - previous)
context = this
args = original_args
// 如果当前调用已经大于上次调用时间 + wait
// 或者用户手动调了时间
// 如果设置了 trailing, 只会进入这个条件
// 如果没有设置 leading, 那么第一次会进入这个条件
// 还有一点, 你可能会觉得开启了定时器那么应该不会进入这个 if 条件了
// 其实还是会进入的, 因为定时器的延时
// 并不是准确的时间, 很可能你设置了2秒
// 但是他需要2.2秒才触发, 这时候就会进入这个条件
if (remaining <= 0 || remaining > wait) {
// 如果存在定时器就清理掉否则会调用二次回调
if (timeout) {
clearTimeout(timeout)
timeout = null
}
previous = now
result = func.apply(context, args)
if (!timeout)
context = args = null
} else if (!timeout && options.trailing !== false) {
// 判断是否设置了定时器和 trailing
// 没有的话就开启一个定时器
// 并且不能不能同时设置 leading 和 trailing
timeout = setTimeout(later, remaining)
}
return result
}
}
Animation Frame Throttling
function useAnimation() {
const frameId = useRef(0)
const ticking = useRef(false)
const handleResize = (event) => {
if (ticking.current)
return
ticking.current = true
frameId.current = requestAnimationFrame(() => handleUpdate(event))
}
const handleUpdate = (event) => {
console.log('resize update')
ticking.current = false
}
useMount(() => {
window.addEventListener('resize', handleResize)
handleUpdate()
return () => {
window.removeEventListener('resize', handleResize)
cancelAnimationFrame(frameId.current)
}
})
}
Event Delegation
- 事件委托利用的是事件冒泡机制, 只制定一事件处理程序, 就可以管理某一类型的所有事件.
- Increases performance and reduces memory consumption:
- 使用事件委托, 只需在 DOM 树中尽量最高的层次上添加一个事件处理程序.
- No need to register new event listeners for newer children.
- DOM Event: Event Capturing (default false) -> Event Target -> Event Bubbling (default true).
window.onload = function () {
const oUl = document.getElementById('ul')
const aLi = oUl.getElementsByTagName('li')
oUl.onmouseover = function (e) {
const e = e || window.event
const target = e.target || e.srcElement
// alert(target.innerHTML);
if (target.nodeName.toLowerCase() === 'li')
target.style.background = 'red'
// 阻止默认行为并取消冒泡
if (typeof e.preventDefault === 'function') {
e.preventDefault()
e.stopPropagation()
} else {
e.returnValue = false
e.cancelBubble = true
}
}
oUl.onmouseout = function (e) {
const e = e || window.event
const target = e.target || e.srcElement
// alert(target.innerHTML);
if (target.nodeName.toLowerCase() === 'li')
target.style.background = ''
// 阻止默认行为并取消冒泡
if (typeof e.preventDefault === 'function') {
e.preventDefault()
e.stopPropagation()
} else {
e.returnValue = false
e.cancelBubble = true
}
}
}
DOM Performance
- 局部变量缓存 DOM 元素.
- 局部变量缓存布局信息.
const btn = document.getElementById('btn')
- HTML Collection 转化成数组再操作.
function toArray(coll) {
for (let i = 0, a = [], len = coll.length; i < len; i++)
a[i] = coll[i]
return a
}
children优于childNodes.childElementCount优于childNodes.length.firstElementChild优于firstChild.lastElementChild优于lastChild.nextElementSibling优于nextSibling优于childNodes[next].previousElementSibling优于previousSibling.
Layout and Paint Performance
- 重排 (
reflow): 重新构造渲染树, 从layout阶段开始. - 重绘 (
repaint): 重新绘制受影响部分, 从paint或composite阶段开始.
获取或改变布局的操作会导致渲染树变化队列刷新, 执行渲染队列中的待处理变化, 重排 DOM 元素.
DOM Manipulation Performance
- 先
display="none", 修改完成后,display="". - 使待修改 DOM 元素脱离标准文档流(改变布局/定位方式), 可减少其他元素的重绘次数.
document.createDocumentFragment().
const fragment = document.createDocumentFragment()
appendDataToElement(fragment, data)
document.getElementById('myList').appendChild(fragment)
- oldNode.cloneNode(true);
const old = document.getElementById('myList')
const clone = old.cloneNode(true)
appendDataToElement(clone, data)
old.parentNode.replaceChild(clone, old)
Animation Frame Performance
run scripts as early as possible:
requestAnimationFrame() runs after the CPU work is done (UI events and JS scripts),
and just before the frame is rendered (layout, paint, composite etc.).
CSSOM Performance
在 js 中(除定位属性) 外, 不直接操作 element.style.attr/element.cssText:
element.classList.add('className')
element.className += ' className'
Script -> Style -> Layout -> Paint -> Composite.
Make script stage become: read then write.
Interleaved read and write will trigger multiple times
of re-layout/repaint/re-composite.
read css -> write css (re-layout/paint/composite) -> read css -> write css (re-layout/paint/composite) -> read css -> write css (re-layout/paint/composite).
read css -> write css (only re-layout/paint/composite once).
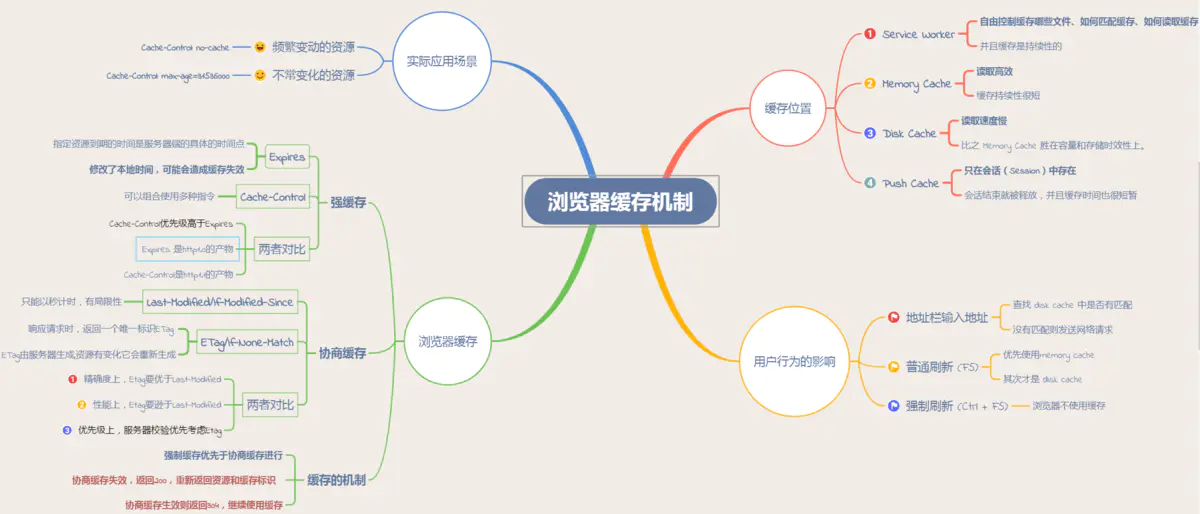
Browser Caches
Browser caches 从缓存位置上来说分为四种, 并且各自有优先级, 当依次查找缓存且都没有命中的时候, 才会去请求网络:
- Service Worker: PWA.
- (In-) Memory Cache: reload Tab page.
- (On-) Disk Cache: big files.
- Push Cache: HTTP/2.
globalThis.addEventListener('install', (event) => {
async function buildCache() {
const cache = await caches.open(cacheName)
return cache.addAll(['/main.css', '/main.mjs', '/offline.html'])
}
event.waitUntil(buildCache())
})
globalThis.addEventListener('fetch', (event) => {
async function cachedFetch(event) {
const cache = await caches.open(cacheName)
let response = await cache.match(event.request)
if (response)
return response
response = await fetch(event.request)
cache.put(event.request, response.clone())
return response
}
event.respondWith(cachedFetch(event))
})
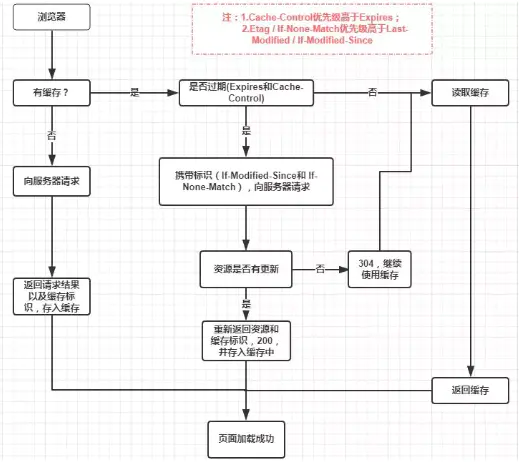
HTTP Cache
浏览器缓存, 也称 HTTP 缓存,
分为强缓存和协商缓存.
优先级较高的是强缓存,
在命中强缓存失败的情况下或者
Cache-Control: no-cache (no-cache allows caches but requires revalidate) 时,
才会走协商缓存.
Local Cache
强缓存是利用 HTTP 头中的 Expires 和 Cache-Control 两个字段来控制的.
强缓存中, 当请求再次发出时, 浏览器会根据其中的 Expires 和 Cache-Control 判断目标资源是否 命中 强缓存,
若命中则直接从缓存中获取资源, 不会再与服务端发生通信.
Cache-Control 相对于 Expires 更加准确, 它的优先级也更高,
当 Cache-Control 与 Expires 同时出现时, 以 Cache-Control 为准.
Expires: Wed, 12 Sep 2019 06:12:18 GMT
Cache-Control: max-age=31536000
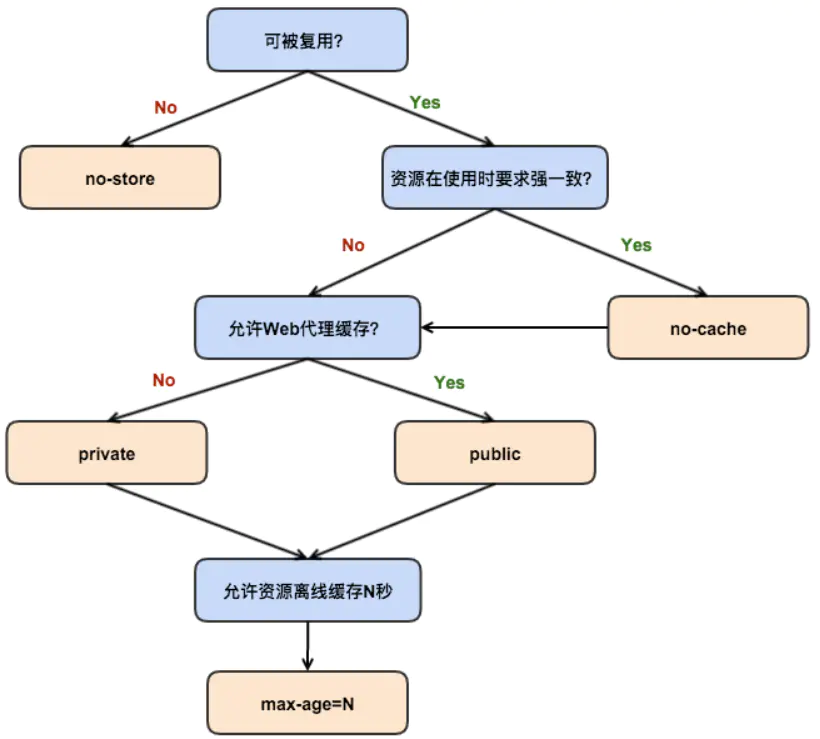
Cache-Control directives:
public: 允许代理服务器缓存资源.private: 不允许代理服务器缓存资源, 只有浏览器可以缓存.immutable: 就算过期了也不用协商, 资源就是不变的.max-age=<time>: 资源过期时间 (浏览器计算), 比Expires精准 (服务器计算).s-maxage=<time>: 代理服务器的资源过期时间.max-stale=<time>: 允许使用过期资源, 指定允许时间.stale-while-revalidate=<time>: 在验证 (协商) 期间, 返回过期的资源. If the cached page has expired, then it will send a stale version while it revalidate the page in the background. The page load is never blocked for the user, though it won't be perfectly fresh for everyone.stale-if-error=<time>: 验证 (协商) 出错的话, 返回过期的资源.must-revalidate: 强缓存过期后, 强制等待协商缓存, 不允许使用过期资源.no-store: 禁止强缓存和协商缓存.no-cache: 禁止强缓存, 允许协商缓存.
Cache the response of the API request, serve the cached version to any visitor, but automatically revalidate the cached object in the background:
export default async () => {
const resp = await fetch('https://hacker-news.firebaseio.com/v0/topstories.json')
const ids = await resp.json()
const stories = await Promise.all(
ids.slice(0, 100).map(async (id) => {
const story = await fetch(`https://hacker-news.firebaseio.com/v0/item/${id}.json`)
return story.json()
})
)
return new Response(JSON.stringify(stories), {
headers: {
'content-type': 'application/json',
'netlify-cdn-cache-control': 'public, max-age=0, stale-while-revalidate=86400',
},
})
}
Page is stale after 5 minutes, but tells the CDN to return the stale response and regenerate it in the background unless it’s over a week old. A popular page will always be fresh, but a rarely-visited one will not keep re-rendering:
// Tell the browser to always check the freshness of the cache
Astro.response.headers.set('Cache-Control', 'public, max-age=0, must-revalidate')
// Tell the CDN to treat it as fresh for 5 minutes,
// then return a stale version while it revalidate.
Astro.response.headers.set(
'Netlify-CDN-Cache-Control',
'public, s-maxage=604800, stale-while-revalidate=604800'
)
Server Cache
协商缓存机制下,
浏览器需要向服务器去询问缓存的相关信息,
进而判断是重新发起请求/下载完整的响应,
还是从本地获取缓存的资源.
如果服务端提示缓存资源未改动 (Not Modified),
资源会被重定向到浏览器缓存,
这种情况下网络请求对应的状态码是 304.
Last-Modified 是一个时间戳,
如果启用了协商缓存,
它会在首次请求时随着 response headers 返回:
Last-Modified: Fri, 27 Oct 2017 06:35:57 GMT
随后每次请求时, 会带上一个叫 If-Modified-Since 的时间戳字段,
它的值正是上一次 response 返回给它的 Last-Modified 值:
If-Modified-Since: Fri, 27 Oct 2017 06:35:57 GMT
服务器可能无法正确感知文件的变化 (未实际改动或改动过快),
为了解决这样的问题, Etag 作为 Last-Modified 的补充出现了.
Etag 是由服务器为每个资源生成的唯一的标识字符串,
这个标识字符串可以是基于文件内容编码的,
因此 Etag 能够精准地感知文件的变化.
GET /i/example.gif HTTP 1.1
Host: image.example.com
------
HTTP 1.1 200 OK
Last-Modified: Tue, 12 Dec 2022 03:03:03 GMT
ETag: "10c24bc-4ab-457e1c1f"
Content-Length: 1195
GET /i/example.gif HTTP 1.1
Host: image.example.com
If-Modified-Since: Tue, 12 Dec 2022 03:03:03 GMT
If-None-Match: "10c24bc-4ab-457e1c1f"
------
HTTP 1.1 304 Not Modified
Code Cache
- cold run:
download -> compile -> store into on-disk cache - warm run:
fetch from browser cache -> compile -> store metadata - hot run:
fetch scripts and metadata from browser cache -> skip compile - positive case: IIFE function heuristics
- passive case: too small (
< 1KB) and inline scripts
Render Blocking Resources
Render Blocking Resources Type
Render blocking resources are files that 'press pause' on the critical rendering path. They interrupt one or more of the steps:
- HTML is technically render blocking resources (but not usually the cause of rendering performance problem)
- CSS is render blocking: render tree can't continue until both the CSSOM and DOM are created.
- JavaScript can be render blocking: when browser encounters a script meant to run synchronously, it will stop DOM creation until script finished.
- If CSS appears before a script, the script will not be executed until the CSSOM is created: CSSOM -> CSS block JS -> JS block HTML parser.
- Images and fonts are not render blocking.
Render Blocking Resources Performance
- Reduce CSS and JavaScript bytes.
- Lazy loading non-critical CSS and JavaScript.
- Use the
defer,async, ormoduleattribute on scripts.
Images Performance
- Responsive images with
srcset(LCP):- Modern format: WebP/SVG.
- Correspond size.
- Hero images pre-fetch loading (LCP).
- Offscreen images lazy loading (INP).
- Critical render path blocking images (INP):
- Images compression and minification.
- Images CDN.
- Images placeholder with
aspect-ratio(CLS).
Responsive Images
Responsive images provide 3 ~ 5 different sizes reduce image transfer sizes by average of ~20%:
<picture>
<source
srcset="/media/filename.avif 300w, /media/filename.avif 500w, /media/filename.avif 2000w"
type="image/avif"
sizes="(max-width: 360px) 300px, (max-width: 720px) 500px, 2000px"
/>
<source
srcset="/media/filename.webp 300w, /media/filename.webp 500w, /media/filename.webp 2000w"
type="image/webp"
sizes="(max-width: 360px) 300px, (max-width: 720px) 500px, 2000px"
/>
<source
srcset="/media/filename.jpg 300w, /media/filename.jpg 500w, /media/filename.jpg 2000w"
type="image/jpeg"
sizes="(max-width: 360px) 300px, (max-width: 720px) 500px, 2000px"
/>
<img
src="/media/filename.jpg"
srcset="/media/filename.jpg 300w, /media/filename.jpg 500w, /media/filename.jpg 2000w"
sizes="(max-width: 360px) 300px, (max-width: 720px) 500px, 2000px"
alt="Description of the image."
width="2000"
height="1333"
loading="lazy"
decoding="async"
/>
</picture>
<img
src="keyboard-800w.jpg"
alt="A beautiful pink keyboard."
width="400"
height="400"
srcset="keyboard-400w.jpg 400w, keyboard-800w.jpg 800w"
sizes="(max-width: 640px) 400px, 800px"
/>
Pre-fetch Loading Images
<link
rel="preload"
as="image"
href="keyboard.jpg"
imagesrcset="poster_400px.jpg 400w, poster_800px.jpg 800w, poster_1600px.jpg 1600w"
imagesizes="50vw"
/>
Lazy Loading Images
<img
src="donut-800w.jpg"
alt="A delicious pink donut"
width="400"
height="400"
srcset="donut-400w.jpg 400w, donut-800w.jpg 800w"
sizes="(max-width: 640px) 400px, 800px"
loading="lazy"
/>
Placeholder Images
<img
src="donut-800w.jpg"
alt="A delicious donut"
width="400"
height="400"
srcset="donut-400w.jpg 400w, donut-800w.jpg 800w"
sizes="(max-width: 640px) 400px, 800px"
loading="lazy"
decoding="async"
style="background-image: url('data:image/svg+xml;base64,[svg text]'); background-size: cover"
/>
Images Format
mp4 smaller than gif (ffmpeg):
<!-- ffmpeg -i dog.gif dog.mp4 -->
<video autoplay loop muted playsinline>
<source src="dog.mp4" type="video/mp4" />
</video>
WebP 25~35% smaller than jpg/png:
<picture>
<source type="image/webp" srcset="flower.webp" />
<source type="image/jpeg" srcset="flower.jpg" />
<img src="flower.jpg" />
</picture>
Images Compression and Minification
Images Performance Reference
- Images format guide.
- Low effort images optimization tips.
- Images optimization guide.
- Images optimization blog.
- Images optimization book.
- Use image sprites only on HTTP/1 to improve page-load times.
- Avoid using image sprites on HTTP/2.
Legacy sprites optimization:
- 按颜色合并.
- 水平排列合并.
- 避免不必要空白.
- 限制颜色种类.
- 先优化单独图像, 再优化合并图像
Web Loading Performance
Data Preloading
- Generally, preloads will load in order parser gets to them for anything >=
Medium. - Font preloads are probably best towards end of
<head>or beginning of<body>. - Import preloads should be done after
<script>tag that needs the import. - Image preloads will have a low priority (async scripts).
Role of preload scanner is speculative, meaning that it examines raw markup (not scan CSS) in order to find resources to opportunistically fetch before the primary HTML parser would otherwise discover them.
The preload scanner discovers the <img> element
even while rendering and document parsing is blocked,
the preload scanner will discover and fetch the image resource more quickly.
<link rel="modulepreload" href="critical-module.mjs" />
<link rel="preload" as="script" href="critical.js" />
<link rel="preload" as="fetch" href="..." crossorigin />
<link rel="preload" as="font" href="myFont.woff2" type="font/woff2" crossorigin />
<link
rel="preload"
as="image"
href="keyboard.jpg"
imagesrcset="poster_400px.jpg 400w, poster_800px.jpg 800w, poster_1600px.jpg 1600w"
imagesizes="50vw"
/>
<link rel="preload" as="video" href="https://cdn.com/small-file.mp4" />
Preload scanner can be defeated (can't discover resources quickly):
- Injecting resources (scripts/images/styles) into DOM with JavaScript.
- Lazy-loading above-the-fold images or iframes using JavaScript solution.
- Rendering markup on client that contain document sub-resources using JavaScript.
Data PreFetching
Quick Link prefetch:
<link rel="prefetch" href="hero.jpg" as="image" />
Pre-fetch and pre-render pitfalls:
- Avoid prefetching pages for authentication.
- Avoid over-prefetching to limit accidental DOS.
- Avoid prefetching pages key to checkout.
- Avoid prefetching large resources.
- Avoid prefetching cross-origin resources.
Loading Priority
<!-- link: initiate an early fetch but de-prioritize the script -->
<link href="/js/script.js" rel="preload" as="script" fetchpriority="low" />
<!-- img: de-prioritize an image in viewport -->
<!-- that could be otherwise prioritized by the browser -->
<img src="/images/in-viewport-but-unimportant.svg" fetchpriority="low" alt="" />
<!-- script: prioritize critical script -->
<script src="/js/live-chat.js" fetchpriority="high"></script>
<!-- iframe: de-prioritize a third-party embed that’s not essential -->
<iframe src="https://example.com" width="400" height="400" fetchpriority="low"></iframe>
<script>
// Critical Fetch request for article content
fetch('/api/articles.json', { priority: 'high' }).then(/*...*/)
// Request for related content now reduced in priority
fetch('/api/related.json', { priority: 'low' }).then(/*...*/)
</script>
Images Lazy Loading
Lazy Loading Polyfill:
<img data-src="flower.jpg" class="lazyload" />
window.addEventListener('scroll', (event) => {
Array.from(document.querySelectorAll('.lazyload')).forEach((image) => {
if (image.slideIntoView(event.getBoundingClientRect()))
image.setAttribute('src', image.dataset.src)
})
})
Observer Lazy Loading:
const observer = new IntersectionObserver((nodes) => {
nodes.forEach((v) => {
if (v.isIntersecting) {
v.target.src = v.target.dataset.src
observer.unobserve(v.target)
}
})
})
const images = document.querySelectorAll('img.lazyload')
images.forEach(v => observer.observe(v))
Native Lazy Loading:
<img src="flower.jpg" lazyload="auto" />
<img src="flower.jpg" lazyload="on" />
<img src="flower.jpg" lazyload="off" />
JavaScript Lazy Loading
- Script Priorities
async: downloads script during parsing document, but will pause parser to execute script.defer: downloads script during parsing document, and waits until document has finished parsing before executing it.- If the script is independent, use
async. - If the scripts rely on each other, use
defer. - If put JavaScript in
<head>, in such script can't access DOM directly (DOM haven't get parsed). - Lazy loading scripts not execute immediately (Chrome coverage devtools).
<script src="myScript.js"></script>
<script src="myScript.js" async></script>
<script src="myScript.js" defer></script>
const DetailsComponent = lazy(() => import('./details'))
export default function PageComponent() {
return (
<Suspense fallback={<div>Loading...</div>}>
<DetailsComponent />
</Suspense>
)
}
Script Lazy Loading
<html>
<body>
... The full body of the page ...
<script>
window.onload = function () {
const script = document.createElement('script')
script.src = 'all_lazy_20100426.js'
script.async = true
document.documentElement.firstChild.appendChild(script)
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
Script Dynamic Loading
function requireScript(file, callback) {
const script = document.getElementsByTagName('script')[0]
const newJS = document.createElement('script')
// IE
newJS.onreadystatechange = function () {
if (newJS.readyState === 'loaded' || newJS.readyState === 'complete') {
newJS.onreadystatechange = null
callback()
}
}
// others
newJS.onload = function () {
callback()
}
// 添加至 HTML 页面
newJS.src = file
newJS.async = true
script.parentNode.insertBefore(newJS, script)
}
requireScript('the_rest.js', () => {
Application.init()
})
Babel Configuration
modules: alwaysfalse, keepesmfor bundler (e.g webpack) tree shaking.useBuiltIns:entry: 将core-js import替换为特性列表.usage: 按使用引入用到的特性列表.
{
"presets": [
[
"@babel/preset-env",
{
"targets": {
"esmodules": true,
"node": ">= 8",
"browsers": "> 0.25%"
},
"modules": false,
"useBuiltIns": "usage"
}
]
]
}
<script type="module" src="main.mjs"></script>
<script nomodule src="legacy.js"></script>
Data Loading Best Practice
- 非必要静态资源上传 CDN: Client -> CDN Server -> CDN 骨干网络 (极度优化) -> CDN Server -> Server.
- 冷启动开启数据预拉取.
- 页面路由切换时进行数据预拉取 (并缓存数据).
Data Loading Reference
Performance Monitoring
前端性能监控分为两种方式, 一种叫做合成监控 (Synthetic Monitoring, SYN), 另一种是真实用户监控 (Real User Monitoring, RUM).
Synthetic Monitoring
在一个模拟场景里, 去提交一个需要做性能审计的页面, 通过一系列的工具/规则去运行你的页面, 提取一些性能指标, 得出一个审计报告.
常见的工具有 Google 的 Lighthouse, WebPageTest, PageSpeed 等
| 优点 | 缺点 |
|---|---|
| 实现简单 | 无法还原全部真实场景 |
| 能采集到丰富的数据, 如硬件指标或瀑布图 | 登录等场景需要额外解决 |
| 不影响真实用户的访问性能 | 单次数据不够稳定 |
| 可以提供页面加载幻灯片等可视化分析途径 | 数据量较小, 无法发挥更大价值 |
Real User Monitoring
用户在页面访问之后就会产生各种各样的性能指标, 之后会将这些性能指标上传的我们的日志服务器上, 进行数据的提起清洗加工, 最后在监控平台上进行展示和分析的一个过程.
- 真实用户监控的优缺点
| 优点 | 缺点 |
|---|---|
| 无需配置模拟条件, 完全还原真实场景 | 影响真实用户的访问性能及流量消耗 |
| 不存在登录等需要额外解决的场景 | 无法采集硬件相关指标 |
| 数据样本足够庞大, 可以减少统计误差 | 无法采集完整的资源加载瀑布图 |
| 新年数据可与其它数据关联, 产生更大价值 | 无法可视化展示加载过程 |
SYN and RUM
| 对比项 | 合成监控 | 真实用户监控 |
|---|---|---|
| 实现难度及成本 | 较低 | 较高 |
| 采集数据丰富度 | 丰富 | 基础 |
| 数据样本量 | 较小 | 大(视业务体量) |
| 适合场景 | 定性分析, 小数据量分析 | 定量分析, 业务数据深度挖掘 |
Monitoring Methods
在真实用户性能数据采集时, 要关注四个方面的东西:
- 使用标准的 API.
- 定义合适的指标.
- 采集正确的数据.
- 上报关联的维度.
Monitoring Standard API
采集性能数据时先抹平 Navigation Timing spec 差异 优先使用 PerformanceTimeline API (在复杂场景, 亦可考虑优先使用 PerformanceObserver):
- 重定向耗时 = redirectEnd - redirectStart.
- DNS 查询耗时 = domainLookupEnd - domainLookupStart.
- TCP 链接耗时 = connectEnd - connectStart.
- HTTP 请求耗时 = responseEnd - responseStart.
- 解析 DOM 树耗时 = domComplete - domInteractive.
- 白屏时间 = responseStart - navigationStart.
- DOMReady 时间 = domContentLoadedEventEnd - navigationStart.
- onload 时间 = loadEventEnd - navigationStart.
Monitoring Statistics Data
First Meaningful Paint: 首次有效渲染时长, 它的一个核心的想法是渲染并不一定代表着用户看到了主要内容, Load 也不一定代表用户看到主要内容. 假设当一个网页的 DOM 结构发生剧烈的变化的时候, 就是这个网页主要内容出现的时候, 那么在这样的一个时间点上, 就是用户看到主要内容的一个时间点.
它的优点是相对校准的估算出内容渲染时间, 贴近用户感知. 但缺点是无原生 API 支持, 算法推导时 DOM 节点含权重.
- First Paint (FP): 0 ~ 1 ~ 2.5s.
- First Meaningful Paint (FMP)
- First Contentful Paint (FCP): 0 ~ 2 ~ 4s.
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): 0 ~ 2.5 ~ 4s.
- Interaction to Next Paint (INP): 0 ~ 0.2 ~ 0.5s.
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): 0 ~ 0.1 ~ 0.25.
- Time to Interactive (TTI): 0 ~ 3.8 ~ 7.3s.
Monitoring Report Dimension
不同的页面操作/页面打开方式/浏览器环境都会对我们页面加载的性能会有影响, 需要上报这些维度的数据, 以便深入性能分析:
- 当前页面是否可见.
- 页面加载方式: 直接打开/刷新打开/前进后退打开.
- 是否启用 HTTP2.
- 是否启用 Service Worker.
Monitoring Report Performance
解决上报对性能的影响问题有以下方案:
- 延迟合并上报: 延迟到
onload事件后, 并合并多个上报请求. - 使用 Beacon API:
- Sent reliably (even if page unload).
- Sent asynchronously.
- Not impact loading of next page.
- 使用
post上报. - Prefer
visibilitychange/pagehideevent.unload/beforeunloadevent not precise for mobile users: e.g switch to another app not triggerunloadevent.
document.addEventListener('DOMContentLoaded', () => {
console.log('DOM 挂载时间: ', Date.now() - timerStart)
// 性能日志上报...
})
window.addEventListener('load', () => {
console.log('所有资源加载完成时间: ', Date.now() - timerStart)
// 性能日志上报...
})
document.addEventListener('visibilitychange', () => {
if (document.visibilityState === 'hidden') {
const obj = { user: 1 }
const blob = new Blob([JSON.stringify(obj, null, 2)], {
type: 'application/json',
})
navigator.sendBeacon('/log', blob)
}
})
GIF Image Beacon
使用 GIF 图片进行前端监控上报:
- 跨域友好:
img天然支持跨域. - 节省网络资源:
- 图片请求不占用 AJAX 请求限额.
GIF简单安全, 体积小, 对网页内容几乎无影响, 相较BMP/PNG, 可以节约41%/35%网络资源.
- 不会阻塞页面加载, 不影响用户体验:
只需
new Image()对象, 通过onerror和onload事件来检测发送状态, 一般情况下无需append到DOM中.
const thisPage = window.location.href
const referringPage = document.referrer ? document.referrer : 'none'
const beacon = new Image()
beacon.src = `http://www.example.com/logger/beacon.gif?page=${encodeURI(
thisPage,
)}&ref=${encodeURI(referringPage)}`
Performance Monitoring Reference
- Performance monitoring data collection and report case.
- Performance monitoring real world case.
- Dangerous performance cheating hacks.
Web Vitals
Web Performance API
performance.mark('mainThread-start')
expensiveCalculation()
performance.mark('mainThread-stop')
performance.measure('mainThread', 'mainThread-start', 'mainThread-stop')
// 计算加载时间.
function getPerformanceTiming() {
const performance = window.performance
if (!performance) {
// 当前浏览器不支持.
console.log('你的浏览器不支持 performance 接口')
return
}
const t = performance.timing
const times = {}
// 【重要】页面加载完成的时间.
// 【原因】几乎代表了用户等待页面可用的时间.
times.loadPage = t.loadEventEnd - t.navigationStart
// 【重要】解析 DOM 树结构的时间.
// 【原因】DOM 树嵌套过多.
times.domReady = t.domComplete - t.responseEnd
// 【重要】重定向的时间.
// 【原因】拒绝重定向. e.g http://example.com/ 不应写成 http://example.com.
times.redirect = t.redirectEnd - t.redirectStart
// 【重要】DNS 查询时间.
// 【原因】DNS 预加载做了么? 页面内是不是使用了太多不同的域名导致域名查询的时间太长?
// 可使用 HTML5 Prefetch 预查询 DNS, 见: [HTML5 prefetch](http://segmentfault.com/a/1190000000633364).
times.lookupDomain = t.domainLookupEnd - t.domainLookupStart
// 【重要】读取页面第一个字节的时间.
// 【原因】这可以理解为用户拿到你的资源占用的时间, 加异地机房了么, 加CDN 处理了么? 加带宽了么? 加 CPU 运算速度了么?
// TTFB 即 Time To First Byte 的意思.
// 维基百科: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Time_To_First_Byte.
times.ttfb = t.responseStart - t.navigationStart
// 【重要】内容加载完成的时间.
// 【原因】页面内容经过 gzip 压缩了么, 静态资源 `CSS`/`JS` 等压缩了么?
times.request = t.responseEnd - t.requestStart
// 【重要】执行 onload 回调函数的时间.
// 【原因】是否太多不必要的操作都放到 onload 回调函数里执行了, 考虑过延迟加载/按需加载的策略么?
times.loadEvent = t.loadEventEnd - t.loadEventStart
// DNS 缓存时间.
times.appCache = t.domainLookupStart - t.fetchStart
// 卸载页面的时间.
times.unloadEvent = t.unloadEventEnd - t.unloadEventStart
// TCP 建立连接完成握手的时间.
times.connect = t.connectEnd - t.connectStart
return times
}
const [pageNav] = performance.getEntriesByType('navigation')
// Measuring DNS lookup time.
const totalLookupTime = pageNav.domainLookupEnd - pageNav.domainLookupStart
// Quantifying total connection time.
const connectionTime = pageNav.connectEnd - pageNav.connectStart
let tlsTime = 0 // <-- Assume 0 to start with
// Was there TLS negotiation?
if (pageNav.secureConnectionStart > 0) {
// Awesome! Calculate it!
tlsTime = pageNav.connectEnd - pageNav.secureConnectionStart
}
// Cache seek plus response time of the current document.
const fetchTime = pageNav.responseEnd - pageNav.fetchStart
// Service worker time plus response time.
let workerTime = 0
if (pageNav.workerStart > 0)
workerTime = pageNav.responseEnd - pageNav.workerStart
// Request time only (excluding redirects, DNS, and connection/TLS time).
const requestTime = pageNav.responseStart - pageNav.requestStart
// Response time only (download).
const responseTime = pageNav.responseEnd - pageNav.responseStart
// Request + response time.
const requestResponseTime = pageNav.responseEnd - pageNav.requestStart
FP
First paint time:
function entryHandler(list) {
for (const entry of list.getEntries()) {
if (entry.name === 'first-paint')
observer.disconnect()
console.log(entry)
}
}
const observer = new PerformanceObserver(entryHandler)
observer.observe({ type: 'paint', buffered: true })
// {
// duration: 0,
// entryType: "paint",
// name: "first-paint",
// startTime: 359,
// }
FCP
First Contentful Paint:
- Add the
deferorasyncattributes to<script>tags. - Minify the JavaScript and CSS files.
- Remove unused CSS (e.g Tailwind.css JIT mode).
- Lazy importing components not for first page.
- Server side rendering.
- Reduce server response time (e.g CDN).
- TBT (Total Blocking Time) = TTI (Time to Interactive) - FCP (First Contentful Paint).
function entryHandler(list) {
for (const entry of list.getEntries()) {
if (entry.name === 'first-contentful-paint')
observer.disconnect()
console.log(entry)
}
}
const observer = new PerformanceObserver(entryHandler)
observer.observe({ type: 'paint', buffered: true })
// {
// duration: 0,
// entryType: "paint",
// name: "first-contentful-paint",
// startTime: 459,
// }
LCP
Largest Contentful Paint:
- Use a CDN for assets like images and video.
- Compress images:
- Minify images.
- Convert images from JPEG/PNG to WebP.
- Responsive images:
size image based on device size with
srcseton<img>or<picture>. - 渐进渲染是提高
SpeedIndex关键: 结合Suspense优先渲染已准备好的视图, 渐进渲染等待数据的视图. - LCP optimization checklist.
- LCP optimization guide.
function entryHandler(list) {
if (observer)
observer.disconnect()
for (const entry of list.getEntries())
console.log(entry)
}
const observer = new PerformanceObserver(entryHandler)
observer.observe({ type: 'largest-contentful-paint', buffered: true })
// {
// duration: 0,
// element: p,
// entryType: 'largest-contentful-paint',
// id: '',
// loadTime: 0,
// name: '',
// renderTime: 1021.299,
// size: 37932,
// startTime: 1021.299,
// url: '',
// }
Emulate slow third-party resources with Playwright:
import { expect, test } from '@playwright/test'
test('works with slows resources', async ({ page }) => {
page.route(
'**',
route =>
new Promise((resolve) => {
const requestURL = route.request().url()
if (requestURL.match(/http:\/\/localhost:8080/)) {
resolve(route.continue())
} else {
setTimeout(() => {
console.log(`Delaying ${requestURL}`)
resolve(route.continue())
}, 10000)
}
}),
)
await page.goto('http://localhost:8080')
const largestContentfulPaint = await page.evaluate(() => {
return new Promise((resolve) => {
new PerformanceObserver((l) => {
const entries = l.getEntries()
// the last entry is the largest contentful paint
const largestPaintEntry = entries.at(-1)
resolve(largestPaintEntry.startTime)
}).observe({
type: 'largest-contentful-paint',
buffered: true,
})
})
})
console.log(`CLP: ${Number.parseFloat(largestContentfulPaint)}ms`)
// Expect a title "to contain" a substring.
await expect(page).toHaveTitle(/Frontend downtime/)
})
INP
Interaction to Next Paint (INP) 已取代 FID, 成为 Core Web Vitals 的一部分:
- It considers the time between user's interaction and the next paint.
- Input delay: callback queue blocked by other higher priority tasks.
- Processing time: event handler execution time.
- Presentation delay: rendering and compositing time.
Improve INP for Vanilla.js:
- Reduce: 减少不必要的代码, e.g Useless polyfills, redundant animation and transition effects.
- Defer:
推迟不需要在下一个绘制之前运行的代码,
e.g Lazy loading, code splitting,
defer irrelevant expensive calculations (
requestIdleCallback()). - Optimize:
优化必须在下一个绘制之前运行的代码,
e.g Debounce, throttle, virtualized Window, time slicing (
yieldToMain()).
Improve INP in Next.js:
- Concurrent rendering with
useTransitionhook. - Leverage automatic batching.
- Selective hydration pattern.
- Leverage SSG and ISR for static content.
- Offloading heavy computations to Web Workers.
- Prevent unnecessary re-renders with
Forget Compilerand state management library.
CLS
Cumulative Layout Shift:
- Set
heightandwidthattributes of image or video, so that it won’t move content around it once it’s loaded. - Avoid using
popupsoroverlaysunless they appear when the user interacts with the page. - When it’s necessary to move elements, use
transformanimations.
let sessionValue = 0
let sessionEntries = []
const cls = {
subType: 'layout-shift',
name: 'layout-shift',
type: 'performance',
pageURL: getPageURL(),
value: 0,
}
function entryHandler(list) {
for (const entry of list.getEntries()) {
// Only count layout shifts without recent user input.
if (!entry.hadRecentInput) {
const firstSessionEntry = sessionEntries[0]
const lastSessionEntry = sessionEntries[sessionEntries.length - 1]
// If the entry occurred less than 1 second after the previous entry and
// less than 5 seconds after the first entry in the session, include the
// entry in the current session. Otherwise, start a new session.
if (
sessionValue
&& entry.startTime - lastSessionEntry.startTime < 1000
&& entry.startTime - firstSessionEntry.startTime < 5000
) {
sessionValue += entry.value
sessionEntries.push(formatCLSEntry(entry))
} else {
sessionValue = entry.value
sessionEntries = [formatCLSEntry(entry)]
}
// If the current session value is larger than the current CLS value,
// update CLS and the entries contributing to it.
if (sessionValue > cls.value) {
cls.value = sessionValue
cls.entries = sessionEntries
cls.startTime = performance.now()
lazyReportCache(deepCopy(cls))
}
}
}
}
const observer = new PerformanceObserver(entryHandler)
observer.observe({ type: 'layout-shift', buffered: true })
// {
// duration: 0,
// entryType: "layout-shift",
// hadRecentInput: false,
// lastInputTime: 0,
// name: "",
// sources: (2) [LayoutShiftAttribution, LayoutShiftAttribution],
// startTime: 1176.199999999255,
// value: 0.000005752046026677329,
// }
Core Web Vitals
Google Core Web Vitals:
- 加载 (Loading): LCP.
- 交互 (Interactivity): INP.
- 视觉稳定 (Visual Stability): CLS.
Web Vitals Reference
- LCP optimization guide.
- INP optimization guide.
- CLS optimization guide.
- Web latency guide.
- Web vitals measurement best practices.
- Web vitals field data debugging guide.
- Web vitals real world case.
PRPL Pattern
PRPL pattern focuses on 4 main performance considerations:
- Pushing critical resources efficiently: minimize amount of round trips to server and reducing loading time.
- Rendering initial route soon as possible: improve user experience.
- Pre-caching assets in the background for frequently visited routes: minimize amount of requests to server and enable better offline experience.
- Lazily loading routes and assets that aren’t requested as frequently.
Performance Best Practice
- Code optimization:
- Fast CSS styles:
CSS Performance. - Fast JavaScript code (
Effective JavaScript):- DOM performance.
- React performance.
- Concurrency: asynchronous/web worker.
- Use monomorphic objects due to shape and inline caches.
- Use monomorphic function in hot code paths.
- Fast CSS styles:
- Resources optimization (HTML/CSS/JS/Images/Audio/Video/Fonts):
- Remove useless files: Chrome devtool code coverage panel.
- Code splitting: Webpack
splitChunks. - Tree shaking.
- Gzip/Brotli (
Accept-Encoding/Content-Encoding). - CDN: faster resources.
- Loading performance:
- PreFetch/PreLoad/PreRendering (SSR).
- Lazy loading: HTML/CSS/JS/Images/Audio/Video/Fonts.
- Resources priority hints.
- Resources loading hints.
- Web caching:
- Offline caching: PWA.
- HTTP caching: 强缓存与协商缓存.
- CDN: shared public caches.
- Network protocols performance:
- Reducing HTTP requests.
- 重用 TCP 连接.
- 多路复用.
- 减少传输冗余资源.
- Caching and reducing DNS lookups:
- Remove too much domains.
- HTML5 DNS prefetch.
- Avoid HTTP redirects.
- CDN: minimize RTT.
- Reducing HTTP requests.
Performance Tools
Speed tools list:
- WebPageTest
- PageSpeed Insights
- Chrome UX report.
- Chrome DevTools
- LightHouse CI action.
- Chrome audit tab:
- Chrome inspector:
chrome://inspect/#devicesto start inspecting.