Mathematical Analysis
Limit
洛必达法则是求解分数形式的未定型极限 的有效方法之一:
Derivative
常见导数:
Series
泰勒级数利用函数在某点的各阶导数, 近似该点附近函数的值:
Euler's Formula
复数平面 (Complex Plane) 上的圆周运动:
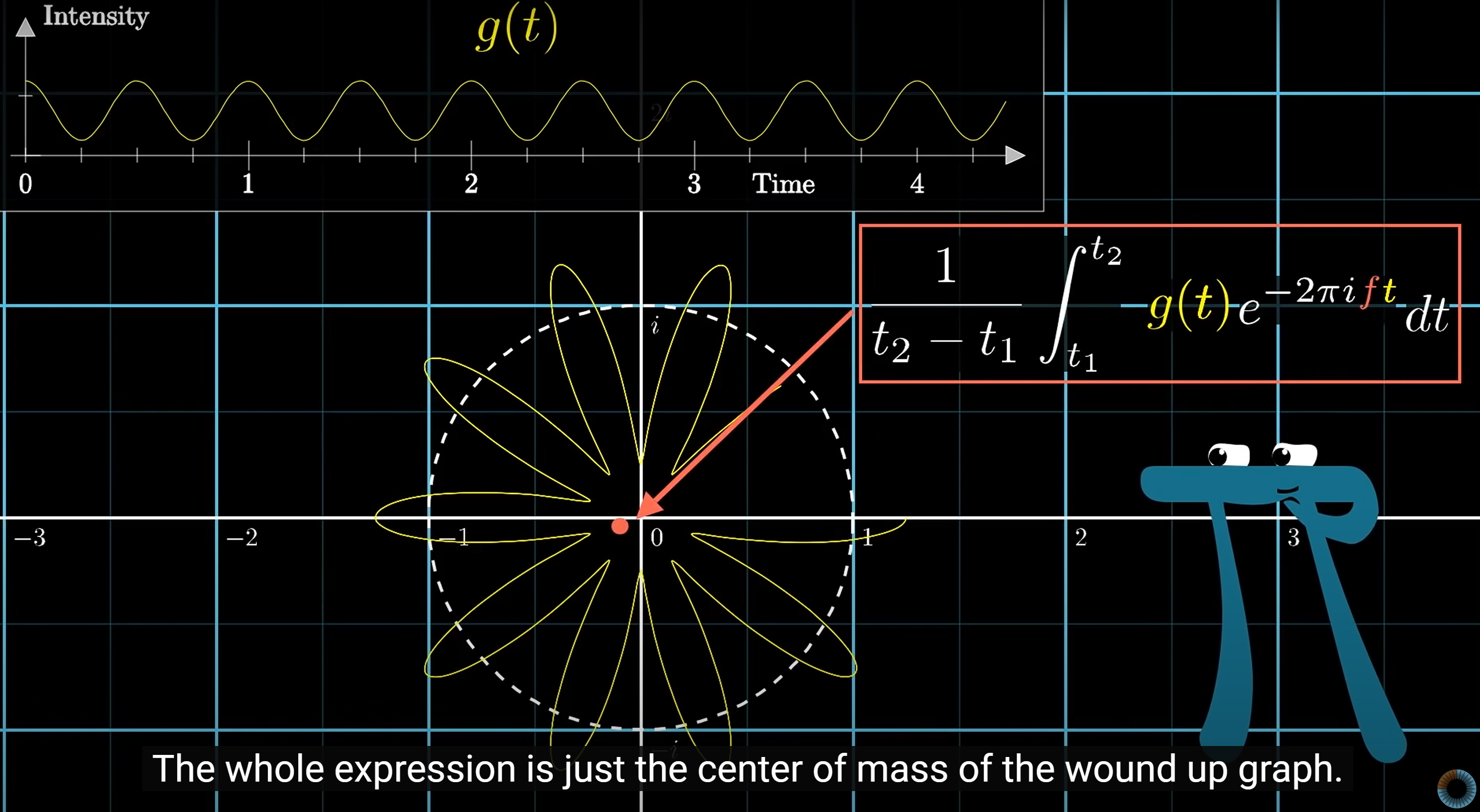
Fourier Transform
Time to frequency transform:
Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT):
outcomes
Differential Equation
微分方程 (Differential Equation) 是描述变量之间关系的方程, 通常包含未知函数及其导数, 用于描述物理现象和自然规律.
First Order Differential Equation
一阶微分方程:
Second Order Differential Equation
Gravitational force equation:
Partial Differential Equation
Black-Scholes / Merton equation:
Phase Space
相空间是描述系统状态的空间, 每个点代表系统的一个状态, 点的轨迹描述了系统的演化.
import numpy as np
# Physical constants
g = 9.8
L = 2
mu = 0.1
THETA_0 = np.pi / 3 # 60 degrees
THETA_DOT_0 = 0 # No initial angular velocity
# Definition of ODE
def get_theta_double_dot(theta, theta_dot):
return -mu * theta_dot - (g / L) * np.sin(theta)
# Solution to the differential equation (numerically)
def theta(t):
theta = THETA_0
theta_dot = THETA_DOT_0
delta_t = 0.01 # Time step
for _ in np.arange(0, t, delta_t):
theta_double_dot = get_theta_double_dot(theta, theta_dot)
theta += theta_dot * delta_t
theta_dot += theta_double_dot * delta_t
return theta