Values
Data Types
CSS data types define typical values (including keywords and units) accepted by CSS properties and functions:
- Textual data types.
- Numeric data types.
- Quantities.
- Combinations of types.
- Color data types.
- Image data types.
- 2D
<position>.
CSS data types list:
- CSS formal syntax.
- CSS values.
- CSS units.
- CSS functions.
Inherit
Inherit from parent.
Initial
The initial value of a CSS property is its default value, as listed in its standard definition table.
Revert
Revert to user agent built in styles.
@supports (-webkit-overflow-scrolling: touch) {
progress {
all: revert;
}
}
Unset
Reset to inherit or initial value.
dialog {
all: unset; /* Exclude `unicode-bidi`, `direction`, custom variables */
}
Specified
The specified value of a CSS property is the value it receives from the document's style sheet
Computed
The computed value of a CSS property is the value that is transferred from parent to child during inheritance. It is calculated from the specified value by:
- Handling the special values
inherit,initial,unset, andrevert - Doing the computation needed to reach the value described in the "Computed value" line in the property's definition table
span {
/* display computed to `block` */
position: absolute;
}
Used
The used value of a CSS property is its value after all calculations have been performed on the computed value:
- The used values of dimensions (e.g., width, line-height) are in pixels
- The used values of shorthand properties (e.g., background) are consistent with those of their component properties (e.g., background-color or background-size) and with position and float
Actual
The actual value of a CSS property is the used value of that property after any necessary approximations have been applied
The user agent performs four steps to calculate a property's actual (final) value:
- the specified value is determined based on the result of cascading, inheritance, or using the initial value.
- the computed value is calculated according to the specification (for example, a span with position: absolute will have its computed display changed to block)
- layout is calculated, resulting in the used value
- the used value is transformed according to the limitations of the local environment, resulting in the actual value
- initial.
- specified.
- computed.
- used.
- actual value.
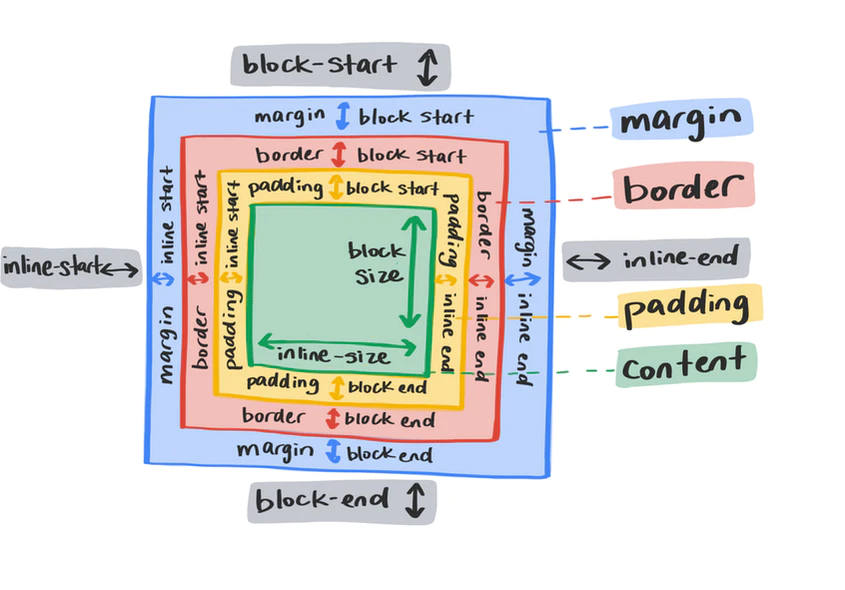
Logical
In position/size/margin/padding/border/text alignment:
block-startfortop.block-endforbottom.blockfor vertical.inline-startforleft.inline-endforright.inlinefor horizontal.
.logical {
/* stylelint-disable shorthand-property-no-redundant-values */
inset-block: 0 0;
inset-inline: 0 0;
inline-size: fit-content;
min-inline-size: min-content;
max-inline-size: max-content;
block-size: fit-content;
min-block-size: min-content;
max-block-size: max-content;
padding-block: 1rem 1rem;
padding-inline: 1rem 1rem;
margin-block: 1rem 1rem;
margin-inline: 1rem 1rem;
border-block-start: 1px solid blue;
border-block-end: 1px solid blue;
border-inline-start: 1px solid blue;
border-inline-end: 1px solid blue;
/* stylelint-enable shorthand-property-no-redundant-values */
}
References
- MDN CSS value formal syntax.
- W3C CSS logical draft.
- CSS logical properties guide.